LMA (laryngeal mask airway) and ETT (endotracheal tube) are the devices used to maintain the airway during general anaesthesia and emergency care. They provide inhaled gases and oxygen to the lungs and also protect from contamination through blood or gastric contents. Over time, various advancements have been made in devices to decrease aspiration, isolate the lungs, and administer medications.
In this article, we’ll do an LMA vs. ETT comparison and know the connection and difference between LMA and ETT.
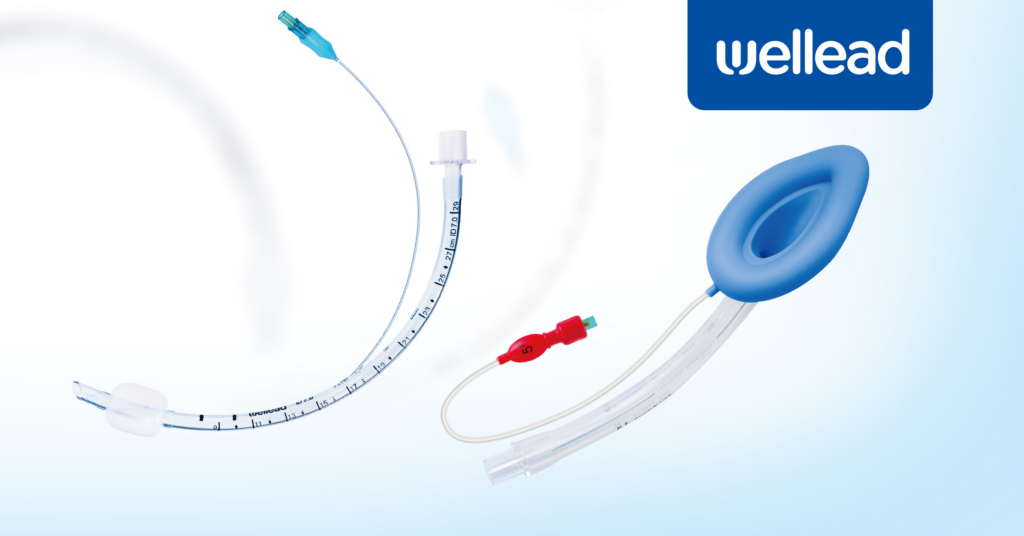
LMA and ETT: Their Connection
Both LMA and ETT have the same purpose, which is to protect the airway, maintain ventilation and oxygenation, and prevent airway obstruction during anaesthesia-requiring procedures and surgeries. Both devices are also used for resuscitation in collapsing patients.
| Shared Goals | Overlapping Functions |
| Provide ventilation and oxygenation | Both are important in airway management. |
| LMA and ETT prevent obstruction of the airway | Both can be used in elective surgeries and emergency settings |
| Both of them support the easy administration of anesthesia | Each supports patient safety as they offer controlled ventilation |
| Help in easy resuscitation during emergencies | / |
There is often a hot discussion about the laryngeal mask vs. endotracheal tube. However, both devices complement each other in clinical practice.
LMA (Laryngeal Mask Airway)
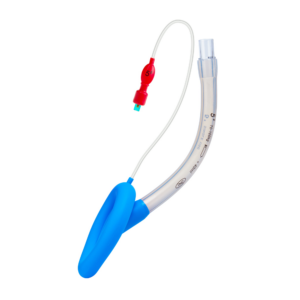
Laryngeal Mask Airway was developed by British Anesthesiologist Dr. Archi Brian in 1981, with the first commercial models introduced in 1988. Since then, its uses have continued to increase.
It is a supraglottic airway device shaped similarly to a large ETT on its proximal end, which is connected with an elliptical mask at the distal end. It is designed to sit in the hypopharynx of the patient, completely covering the supraglottic structures.
Initially, LMA was only used in operating rooms for elective ventilation. In recent years, its application has expanded to emergency and difficult airway scenarios due to ease of insertion and safety, with a high placement success rate in controlled settings.
ETT (Endotracheal Tube)
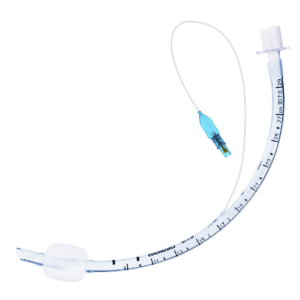
An endotracheal tube is a flexible plastic catheter inserted into the trachea. The use of ETT dates back to the early 1900s. It is placed between the vocal cords through the mouth or nose. Its main purpose is to establish and maintain the patent airway for adequate exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen.
As the advances in surgery and anaesthesia rapidly increased, so did the advancements in ETT. Besides providing the mechanical ventilation, ETT is also used to administer various gases (helium, xenon, nitric oxide, etc), anaesthetic agents (isoflurane, desflurane, or sevoflurane), and certain medications (salbutamol, epinephrine, ipratropium).
LMA vs. ETT: Their Differences
Here is a detailed analysis of major differences between LMA and ETT in terms of methods of operation, clinical indications, and advantages and disadvantages.
| Features | LMA | ETT |
| Placement | Supraglottic (above vocal cords) | Infraglottic (into trachea) |
| Insertion Technique | Blind, simpler | Requires laryngoscopy and skill |
| Airway Protection | Limited against aspiration (in emergency settings) | Full protection |
| Duration of Use | Short, elective procedures | Short to long procedures |
| Ventilation Control | Moderate | Precise, allowing high airway pressures |
| Patient Comfort (post-op) | Less sore throat, less trauma | More discomfort, potential injury |
| Clinical Indications | Elective, less invasive cases | Critical, high-risk, emergency cases |
(1) Operation: LMA vs. ETT
LMA insertion is quicker and less invasive compared to ETT intubation. It can be done without a muscle relaxant, which makes LMA useful in daycare anaesthesia.
On the other hand, ETT intubation provides complete airway control, but clinicians have to be skilled, and the process requires more time and equipment, such as a laryngoscope, syringe for inflation of the cuff, stylet, and suction catheter.
(2) Clinical Indications: LMA vs. ETT
The answer to when to use LMA vs. ETT depends on the condition of the patient and the surgical need.
| LMA Indication | ETT Indication |
| Short elective procedures | Longer surgeries |
| When intubation is not mandatory | Risk of aspiration |
| As a rescue device in failed intubation | Need for mechanical ventilation with high pressures |
| In resource-limited settings, cardiac arrest, pre-hospital care | In hemodynamically unstable patients |
(3) Advantages and Disadvantages of LMA vs. ETT
Various studies have been conducted that show the advantages and disadvantages of the use of LMA vs. ETT in various case scenarios and documenting the results.
LMA
Advantages:
— Rapid insertion; placement and removal are relatively simple and quick.
— Less stimulating, which leads to a more comfortable recovery and a better patient experience.
Disadvantages:
— The LMA may become dislodged or slip out of position during use.
— In some cases, the seal may be poor, making it unsuitable for high-risk patients with gastric retention, pregnancy, or obesity.
ETT
Advantages:
— Compared to the LMA, endotracheal intubation provides a more secure and precise method of airway management. It is suitable for long-duration, complex surgeries and those requiring muscle relaxants.
— ETT has a wider range of indications.
Disadvantages:
— Intubation is more stimulating, which may cause an increase in heart rate and fluctuations in blood pressure.
— Post-operative discomfort is more pronounced.
— The procedure is more difficult to perform than LMA insertion.
Well Lead Medical
Our dedicated team of experts understands the importance of the right airway device to save a patient’s life in any clinical situation.
- That’s why we at Well Lead Medical have a portfolio of a wide range of laryngeal masks that are specifically designed keeping the ease of use and patient comfort in mind.
- Our high-quality endotracheal tubes, including cuffed ETT options, provide secured airway management in complex cases.
Well Lead Medical is a trusted partner in medical device solutions. Our commitment to support clinicians worldwide with safe, reliable, and efficient airway products is what made hundreds and thousands of clinicians trust our products. For more details, please contact us.

