Tracheal tubes are essential components in airway management, used in procedures requiring mechanical ventilation. The two main types of tracheal tubes are cuffed and uncuffed, each serving different needs in clinical settings. Cuffed endotracheal tubes (ETTs) are equipped with an inflatable cuff that creates a seal in the trachea, preventing aspiration and ensuring reliable airflow during mechanical ventilation. Uncuffed tubes, on the other hand, do not have this seal and are typically used in patients with less complex airway management needs. Understanding the differences between cuffed vs uncuffed tracheal tubes is crucial for healthcare providers to make informed decisions based on patient requirements.
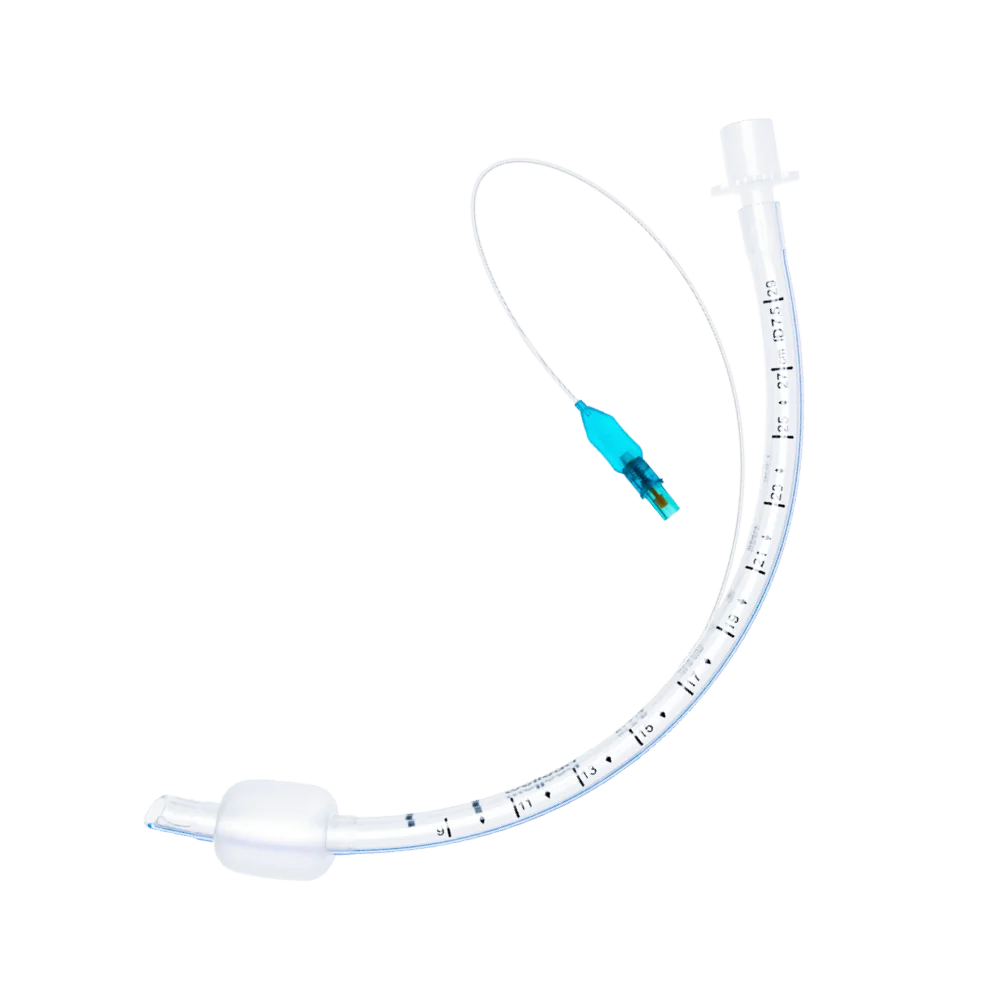
Benefits of Cuffed Endotracheal Tubes by Well Lead Medical
Cuffed endotracheal tubes offer a variety of benefits, particularly in scenarios requiring precise ventilation and aspiration prevention. Well Lead Medical manufactures high-quality cuffed tracheal tubes that help healthcare providers maintain a secure airway for patients undergoing surgery or intensive care. These tubes are designed to create a secure seal, preventing gastric contents or other fluids from entering the lungs, which is critical in preventing aspiration pneumonia. Well Lead Medical’s cuffed tubes are engineered to provide efficient ventilation, allowing for lossless gas transmission and precise control of air pressure, making them ideal for adult patients or those at high risk of aspiration.
Moreover, cuffed tubes help reduce the risk of accidental tube dislodgement, ensuring a stable airway throughout the procedure. However, these tubes must be used with care to avoid over-inflation, which could lead to tracheal damage or discomfort. Well Lead Medical offers cuffed tubes that prioritize both safety and comfort, ensuring a balanced approach to airway management.
The Role of Uncuffed Tracheal Tubes in Pediatric Care
Uncuffed tracheal tubes are traditionally preferred in pediatric care, particularly for children with small airways. The absence of an inflatable cuff in these tubes reduces the risk of tracheal damage, making them a safer option for younger patients. In pediatric patients, the subglottic anatomy is different, and using a cuffed tube may increase the risk of airway injury. Uncuffed tubes also have lower airway resistance, which is beneficial for spontaneously breathing patients, as it allows for easier suctioning and ventilation.
However, one of the primary disadvantages of uncuffed tubes is the increased risk of aspiration due to the lack of a tracheal seal. This can lead to inefficient ventilation and complications like leakage. Despite this, many healthcare providers are moving towards the use of cuffed tracheal tubes for pediatric patients to prevent leaks and improve overall airway protection. Well Lead Medical‘s range of uncuffed tubes offers excellent flexibility for pediatric use, ensuring optimal care for young patients.
Conclusion
So when deciding between cuffed vs uncuffed tracheal tubes, healthcare providers must consider the specific needs of the patient. For adults and patients at risk of aspiration, cuffed tubes from Well Lead Medical provide the security and precision needed. For pediatric care, uncuffed tubes are often the preferred option, offering reduced risk of tracheal injury while requiring careful management to minimize aspiration risks.

