Hydrophilic catheters have transformed the way healthcare professionals approach catheterization, offering significant advantages in terms of comfort and safety. This article provides an in-depth look at hydrophilic catheters how to use them properly, ensuring optimal performance and patient satisfaction.
Understanding Hydrophilic Catheters
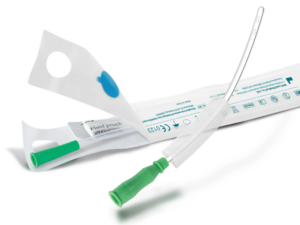
Before delving into hydrophilic catheters how to use them, it is crucial to understand what makes these catheters unique. Hydrophilic catheters are coated with a special material that becomes slippery when exposed to water. This property enhances the ease of insertion and minimizes friction, making them a preferred choice for both intermittent and long-term catheterization.
The smooth surface of hydrophilic catheters significantly reduces the risk of urethral trauma and discomfort during the procedure. This is especially important for patients who may require frequent catheterizations. The hydrophilic coating also helps lower the chances of urinary tract infections (UTIs) by creating a barrier against bacterial adherence, making them a vital tool in patient care.
Steps for Proper Use
Understanding hydrophilic catheters how to use them effectively involves following a series of essential steps. Here’s a guide to ensure safe and efficient catheterization:
1. Preparation: Begin by washing your hands thoroughly with soap and water to prevent infection. Gather all necessary supplies, including the hydrophilic catheter, sterile gloves, and a clean collection container.
2. Hydration: Activate the hydrophilic coating by breaking the water sachet. This step is crucial for ensuring the catheter becomes slippery and easy to insert.
3. Insertion: Just open the package and hold the catheter at the tip and gently insert it into the urethra. The hydrophilic coating should facilitate smooth entry, minimizing discomfort for the patient. If resistance is met, do not force the catheter; instead, withdraw slightly and try again.
4. Collection: Once the catheter is fully inserted, allow urine to drain into the toilet. Ensure that the catheter remains in place during this process.
5. Withdrawal: After the bladder has been fully emptied, gently withdraw the catheter. The hydrophilic coating will help prevent friction upon removal, further enhancing patient comfort.
6. Disposal: Dispose of the catheter according to local regulations for medical waste. Wash your hands thoroughly after the procedure.
By following these steps, healthcare providers can ensure a successful catheterization experience. Training staff on hydrophilic catheters how to use them properly can improve patient outcomes and satisfaction.
Considerations for Effective Catheterization
When discussing hydrophilic catheters how to use them, it is essential to emphasize the importance of proper technique and patient education. Healthcare providers should assess each patient’s specific needs, including catheter size and frequency of use. Well Lead Medical offers a variety of hydrophilic catheters designed to meet diverse clinical requirements, ensuring that healthcare professionals have the right tools for their patients.
Additionally, educating patients on self-catheterization techniques can empower them to manage their conditions more effectively. Providing clear instructions and demonstrations can alleviate anxiety and improve their confidence in using the catheter independently.
Monitoring for any signs of complications, such as pain or unusual discharge, is also critical. Regular follow-ups can help address any issues early, ensuring a smooth catheterization experience.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding hydrophilic catheters and how to use them properly is essential for optimizing patient care and comfort. By following the outlined steps and considering individual patient needs, healthcare providers can enhance the effectiveness of catheterization procedures. With the advancements in hydrophilic catheter technology, such as those offered by Well Lead Medical, the focus remains on improving patient outcomes and satisfaction. Proper training and education are vital components in ensuring that these innovative tools are used effectively, leading to better health management for patients requiring catheterization.

